每一个App在启动时,都会由Zygote fork出一个进程,进程具有独立的资源空间,用于承载App上运行的各种Activity/Service等组件。
当进程创建后就要真正去启动一个App了,那么App的入口函数是什么呢?答案是ActivityThread的main函数。(进程创建后反射调用ActivityThread main函数)
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 public final class ActivityThread
可能有人会认为ActivityThread就是我们常说的主线程或UI线程,但是上面可以看到ActivityThread类是一个final类,也没有继承Thread。因为ActivityThread的Main函数是App的入口函数,那么调用它的线程就是UI线程。
OK,接下来分析一下ActivityThread具体做了些什么
main()函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static void main (String[] args) ...... Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); thread.attach(false ); if (sMainThreadHandler == null ) { sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler(); } Looper.loop(); }
1.主线程初始化 frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public static void prepareMainLooper () prepare(false ); synchronized (Looper.class) { if (sMainLooper != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared." ); } sMainLooper = myLooper(); } } public static void prepare () prepare(true ); } private static void prepare (boolean quitAllowed) if (sThreadLocal.get() != null ) { throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread" ); } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); } public static @Nullable Looper myLooper () { return sThreadLocal.get(); }
从上面的代码中可以看出,主线程初始化时,prepare传入false,而普通线程初始化时传入true,这个参数为quitAllowed,表示线程是否可以退出,主线程无法退出。prepare函数中创建一个Looper对象,并将对象保存在ThreadLocal中。
在prepare之后,又将主线程Looper赋值给了成员变量sMainLooper,这个成员变量的作用是向其他线程提供主线程Looper对象。
1 2 3 4 5 public static Looper getMainLooper () synchronized (Looper.class) { return sMainLooper; } }
这样当我们调用Looper.getMainLooper()时可以获取到主线程的Looper对象了。
2.主线程Handler初始化 在注释2处创建了ActivityThread对象,并获取了主线程的Handler。(attach稍等)
1 2 3 4 final H mH = new H();final Handler getHandler () return mH; }
由此可见主线程的Handler作为ActivityThread的成员变量,是在ActivityThread的main方法被执行,ActivityThread被创建时而初始化。
3.ActivityThread.attch() frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();private void attach (boolean system) ...... final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault(); try { mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } ...... }
ApplicationThread 是ActivityThread内部类,继承自IApplicationThread.Stub,作为服务端接受AMS发出的请求并执行,ApplicationThread是ActivityThread与AMS连接的桥梁。
attch方法实际调用了AMS的attachApplication方法,去看下AMS里的实现
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Override public final void attachApplication (IApplicationThread thread) synchronized (this ) { int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid(); final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid); Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId); } }
AMS中的attachApplicationLocked方法有些复杂,这个流程可以理解为ActivityThread创建时(App启动时)需要向AMS注册自己,用于AMS管理ActivityThread中的所有四大组件的生命周期。
我们看下attachApplicationLocked中的关键部分
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private final boolean attachApplicationLocked (IApplicationThread thread, int pid) ... thread.bindApplication(...); ... if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) { ... } }
3.1 thread.bindApplication AMS通过远程调用,最终又会调用到ActivityThread中ApplicationThread内部类方法。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public final void bindApplication (String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo, List<ProviderInfo> providers, ComponentName instrumentationName, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs, IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher, IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode, boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation, boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map<String, IBinder> services, Bundle coreSettings) if (services != null ) { ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services); } setCoreSettings(coreSettings); AppBindData data = new AppBindData(); data.processName = processName; data.appInfo = appInfo; data.providers = providers; data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName; data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs; data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher; data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection; data.debugMode = debugMode; data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking; data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation; data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode; data.persistent = persistent; data.config = config; data.compatInfo = compatInfo; data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo; sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data); }
在方法中将AMS传递回的数据又发送给主线程中
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 case BIND_APPLICATION: Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication" ); AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj; handleBindApplication(data); Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); break ;
在主线程中调用handleBindApplication处理
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 private void handleBindApplication (AppBindData data) ...... Process.setArgV0(data.processName); android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName(data.processName, UserHandle.myUserId()); TimeZone.setDefault(null ); LocaleList.setDefault(data.config.getLocales()); data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo, data.compatInfo); ...... try { Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null ); mInitialApplication = app; if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) { if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers)) { installContentProviders(app, data.providers); mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT, 10 *1000 ); } } mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs); mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app); } finally { StrictMode.setThreadPolicy(savedPolicy); } }
handleBindApplication中调用LoadedApk类中makeApplication方法
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public Application makeApplication (boolean forceDefaultAppClass, Instrumentation instrumentation) if (mApplication != null ) { return mApplication; } Application app = null ; String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className; if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null )) { appClass = "android.app.Application" ; } try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader(); if (!mPackageName.equals("android" )) { Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "initializeJavaContextClassLoader" ); initializeJavaContextClassLoader(); Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); } ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this ); app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication( cl, appClass, appContext); appContext.setOuterContext(app); } catch (Exception e) { if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) { Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate application " + appClass + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app); mApplication = app; ...... return app; }
到这里应用的Application 就创建出来了,创建Application后再调用callApplicationOnCreate,回调Application的onCreate方法。
3.2 mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app) mStackSupervisor是AMS的成员变量,是Activity堆栈管理辅助类实例
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 boolean attachApplicationLocked (ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException final String processName = app.processName; boolean didSomething = false ; for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1 ; displayNdx >= 0 ; --displayNdx) { ArrayList<ActivityStack> stacks = mActivityDisplays.valueAt(displayNdx).mStacks; for (int stackNdx = stacks.size() - 1 ; stackNdx >= 0 ; --stackNdx) { final ActivityStack stack = stacks.get(stackNdx); if (!isFocusedStack(stack)) { continue ; } ActivityRecord hr = stack.topRunningActivityLocked(); if (hr != null ) { if (hr.app == null && app.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uid && processName.equals(hr.processName)) { try { if (realStartActivityLocked(hr, app, true , true )) { didSomething = true ; } } catch (RemoteException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity " + hr.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e); throw e; } } } } } if (!didSomething) { ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null , 0 , !PRESERVE_WINDOWS); } return didSomething; }
attachApplicationLocked中获取App要启动的top Activity,然后realStartActivityLocked去启动。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 final boolean realStartActivityLocked (ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException ...... app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken, System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration), new Configuration(task.mOverrideConfig), r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage, task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle, r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume, mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo); ...... }
调用ApplicationThread的scheduleLaunchActivity方法
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Override public final void scheduleLaunchActivity (Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident, ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<ReferrerIntent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) ....... sendMessage (H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r) ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: { Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart" ); final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj; r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck( r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo); handleLaunchActivity(r, null , "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY" ); Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
最终调用handleLaunchActivity,最终启动一个Activity
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 private void handleLaunchActivity (ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent); if (a != null ) { r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration); reportSizeConfigurations(r); Bundle oldState = r.state; handleResumeActivity(r.token, false , r.isForward, !r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason); if (!r.activity.mFinished && r.startsNotResumed) { performPauseActivityIfNeeded(r, reason); if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) { r.state = oldState; } } } else { try { ActivityManagerNative.getDefault() .finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null , Activity.DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } }
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 private Activity performLaunchActivity (ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo; if (r.packageInfo == null ) { r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo, Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE); } ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent(); if (component == null ) { component = r.intent.resolveActivity( mInitialApplication.getPackageManager()); r.intent.setComponent(component); } if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null ) { component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName, r.activityInfo.targetActivity); } Activity activity = null ; try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader(); activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity( cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent); StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass()); r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl); r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess(); if (r.state != null ) { r.state.setClassLoader(cl); } } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate activity " + component + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } try { Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false , mInstrumentation); if (activity != null ) { Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity); CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager()); Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration); if (r.overrideConfig != null ) { config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig); } if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity " + r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config); Window window = null ; if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) { window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow; r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null ; r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null ; } activity.attach(appContext, this , getInstrumentation(), r.token, r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent, r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config, r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window); if (customIntent != null ) { activity.mIntent = customIntent; } r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null ; activity.mStartedActivity = false ; int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource(); if (theme != 0 ) { activity.setTheme(theme); } activity.mCalled = false ; if (r.isPersistable()) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } else { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state); } if (!activity.mCalled) { throw new SuperNotCalledException( "Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() + " did not call through to super.onCreate()" ); } r.activity = activity; r.stopped = true ; if (!r.activity.mFinished) { activity.performStart(); r.stopped = false ; } if (!r.activity.mFinished) { if (r.isPersistable()) { if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null ) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } } else if (r.state != null ) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state); } } if (!r.activity.mFinished) { activity.mCalled = false ; if (r.isPersistable()) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } else { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state); } if (!activity.mCalled) { throw new SuperNotCalledException( "Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() + " did not call through to super.onPostCreate()" ); } } } r.paused = true ; mActivities.put(r.token, r); } catch (SuperNotCalledException e) { throw e; } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to start activity " + component + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } return activity; }
后面就交给App里面处理逻辑了。
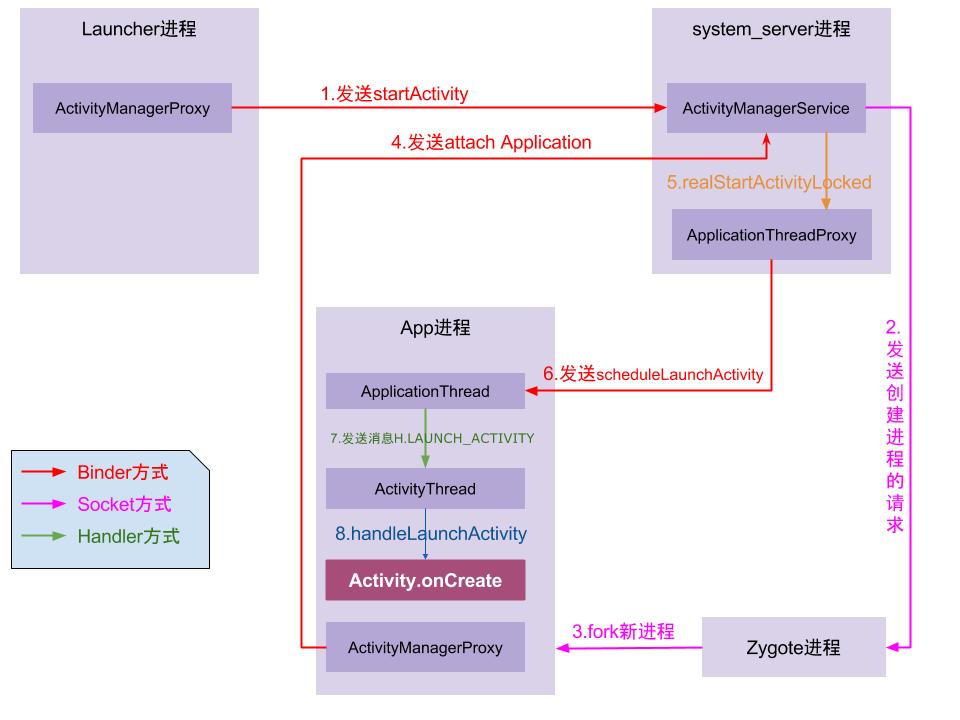
使用gityuan一张图总结一下